Class 11 Informatic practice Revised Syllabus for session 2021-2022: CBSE release class 11 Informatics practice syllabus for class 11 for session 2021-2022. CBSE Reduced syllabus for this session due to COVID 19. In this article we share syllabus released by CBSE and also discuss the practical file program which included by CBSE. Download Class 11 CBSE Informatics practice syllabus for this session. we will provide hand written notes for Term 1 and term 2 examination.
Learning Outcomes
- At the end of this course, students will be able to:
- Identify the components of computer system.
- Create Python programs using different data types, lists and dictionaries.
- Understand database concepts and Relational Database Management Systems.
- Retrieve and manipulate data in RDBMS using Structured Query Language
- Identify the Emerging trends in the fields of Information Technology
Complete syllabus for class 11 for session 2021-2022. Download complete syllabus for class 11 and start preparation for term 1 and term 2. There are only 4 unit in this session which include Introduction of Computer System , Introduction to python.Data base concept and SQL query, Introduction to the Emerging Trends .
Unit 1:
Introduction to Computer System
Introduction to computer and computing: evolution of computing devices, components of a computer system and their
interconnections, Input/output devices.
Computer Memory: Units of memory, types of memory – primary and secondary, data deletion, its recovery and related
security concerns.
Software: purpose and types – system and application software, generic and specific purpose software.
Unit 2:
Introduction to Python
Basics of Python programming, Python interpreter - interactive and script mode, the structure of a program, indentation,
identifiers, keywords, constants, variables, types of operators, precedence of operators, data types, mutable and
immutable data types, statements, expressions, evaluation and comments, input and output statements, data type
conversion, debugging.
Control Statements: if-else, for loop
Lists: list operations - creating, initializing, traversing and manipulating lists, list methods and built-in functions.
Dictionary: concept of key-value pair, creating, initializing, traversing, updating and deleting elements, dictionary methods
and built-in functions.
Unit 3:
Database concepts and the Structured Query Language
Database Concepts: Introduction to database concepts and its need, Database Management System.
Relational data model: Concept of domain, tuple, relation, candidate key, primary key, alternate key
Advantages of using Structured Query Language, Data Definition Language, Data Query Language and Data
Manipulation Language, Introduction to MySQL, creating a database using MySQL, Data Types
Data Definition: CREATE TABLE
Data Query: SELECT, FROM, WHERE.
Data Manipulation: INSERT
Unit 4:
Introduction to the Emerging Trends
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Immersive experience (AR, VR), Robotics, Big data and its characteristics, Internet of Things (IoT), Sensors, Smart cities, Cloud Computing and Cloud Services (SaaS, IaaS,PaaS); Grid Computing, Block chain technology
Distribution of Marks and Periods for this session for Term 1 :
Unit 1:
Introduction to Computer System
Introduction to computers and computing: evolution of computing devices, components of a
computer system and their interconnections, Input/Output devices.
Computer Memory: Units of memory, types of memory – primary and secondary, data deletion, its
recovery and related security concerns.
Software: purpose and types – system and application software, generic and specific purpose
software.
Unit 2:
Introduction to Python
Basics of Python programming, Python interpreter - interactive and script mode, the structure of a
program, indentation, identifiers, keywords, constants, variables, types of operators, precedence of
operators, data types, mutable and immutable data types, statements, expressions, evaluation of
expressions, comments, input and output statements, data type conversion, debugging,
Control statements: if-else, for loop.
List operations - creating, initializing, traversing and manipulating lists, list methods and built-in
functions.: len(), list(), append(), extend(), insert(), count(), find(), remove(), pop(), reverse(), sort(),
sorted(), min(), max(), sum()
Dictionary: concept of key-value pair, creating, initializing, traversing, updating and deleting
elements, dictionary methods and built-in functions: len(), dict(), keys(), values(), items(), get(),
update(), clear(), del()
Programming in Python
1. To find average and grade for given marks.
2. To find the sale price of an item with a given cost and discount (%).
3. To calculate perimeter/circumference and area of shapes such as triangle, rectangle, square and circle.
4. To calculate Simple and Compound interest.
5. To calculate profit-loss for a given Cost and Sell Price.
6. To calculate EMI for Amount, Period and Interest.
7. To calculate tax - GST / Income Tax.
8. To find the largest and smallest numbers in a list.
9. To find the third largest/smallest number in a list.
10. To find the sum of squares of the first 100 natural numbers.
11. To print the first ‘n’ multiples of a given number.
12. To count the number of vowels in a user entered string.
13. To print the words starting with a particular alphabet in a user entered string.
14. To print the number of occurrences of a given alphabet in a given string.
15. Create a dictionary to store names of states and their capitals.
16. Create a dictionary of students to store names and marks obtained in 5 subjects.
17. To print the highest and lowest values in the dictionary
Term 2 Syllabus for Examination:
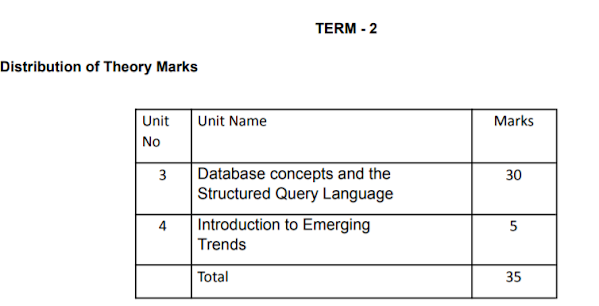
Unit 3:
Database concepts and the Structured Query Language
- Database Concepts: Introduction to database concepts and its need, Database Management System. Relational data model: concept of attribute, domain, tuple, relation, candidate key, primary key, alternate key, foreign key.
- Structured Query Language: Data Definition Language, Data Query Language and Data
- Manipulation Language, Introduction to MySQL: Creating a database, using database, showing tables using MySQL,
- Data Types : char, varchar, int, float, date.
- Data Definition Commands: CREATE, DROP, ALTER (Add and Remove primary key, attribute). Data Query Commands: SELECT-FROM- WHERE, LIKE, BETWEEN, IN, ORDER BY, using arithmetic, logical, relational operators and NULL values in queries, Distinct clause Data Manipulation Commands: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE.
Unit 4:
Introduction to the Emerging Trends
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing,
- Immersive experience (AR, VR), Robotics
- Big data and its characteristics, Internet of Things (IoT), Sensors, Smart cities,
- Cloud Computing and Cloud Services (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS);
- Grid Computing, Block chain technology.
Practical List for term 2:
Data Management: SQL Commands
1. To create a database
2. To create a student table with the student id, class, section, gender, name, dob, and marks as
attributes where the student id is the primary key.
3. To insert the details of at least 10 students in the above table.
4. To delete the details of a particular student in the above table.
5. To increase marks by 5% for those students who have Rno more than 20.
6. To display the entire content of the table.
7. To display Rno, Name and Marks of those students who are scoring marks more than 50. 8. To find the average of marks from the student table.
9. To find the number of students, who are from section ‘A’.
10. To add a new column email in the above table with appropriate data type.
11. To add the email ids of each student in the previously created email column.
12. To display the information of all the students, whose name starts with ‘AN’ (Examples: ANAND,
ANGAD,..)
13. To display Rno, Name, DOB of those students who are born between ‘2005- 01-01’ and
‘2005-12-31’.
14. To display Rno, Name, DOB, Marks, Email of those male students in ascending order of their
names.
15. To display Rno, Gender, Name, DOB, Marks, Email in descending order of their marks. 16. To display the unique section available in the table.
Click on download button to download Class 11 syllabus for session 2021-2022
class 11 ip term 1 syllabus 2021 22 ip class 11 term 1 syllabus class xi ip syllabus class 11 ip syllabus term 1 syllabus class 11 cbse 2021-22 ip class 11 term 1 syllabus pdf class 11 term 1 syllabus pdf download class 11 ip syllabus 2021-22 term 1 class 11 first term syllabus












.png)

.png)
![[Practical File] Informatics Practices Class 12 Code 065 Term 2](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiqeB8knLwYOTMrphMRYyRXmbHe9V34AFIA9dIWKLWX5x-fL6rdb38pgsEG7epekeGO1EU5Z7BLdrweyWtiQ25k4Z7-bxvIMRhQPvNXvJAbKSB31qOfXlhJ1bBW-1E1dfdS3CY-utwvy6Km8-qjW4vFAU98OcMd6tkA0rBWAoGMMETdju6cMlTlii4Q/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/Purple%20Neon%20Gaming%20Channel%20Youtube%20Intro.jpg)


0 Comments